Category: corpus linguistics
Data-driven learning in informal contexts?
Recent DDL research & events: 5 tips
Really exciting times for DDL and corpus linguistics and education researchers. There’s some interesting new stuff that has just been published, including some interesting conference videos. Here’s my selection.
(1) Boulton, A., & Vyatkina, N. (2021). Thirty years of data-driven learning: Taking stock and charting new directions over time. Language Learning & Technology, 25(3), 66-89.
Abstract
The tools and techniques of corpus linguistics have many uses in language pedagogy, most directly with language teachers and learners searching and using corpora themselves. This is often associated with work by Tim Johns who used the term Data-Driven Learning (DDL) back in 1990. This paper examines the growing body of empirical research in DDL over three decades (1989-2019), with rigorous trawls
uncovering 489 separate publications, including 117 in internationally ranked journals, all divided into five time periods. Following a brief overview of previous syntheses, the study introduces our collection, outlining the coding procedures and conversion into a corpus of over 2.5 million words. The main part of the analysis focuses on the concluding sections of the papers to see what recommendations and future avenues of research are proposed in each time period. We use manual coding and semi-automated corpus keyword analysis to explore whether those points are in fact addressed in later publications as an indication of the evolution of the field
(2) Dr Peter Crosthwaite, The University of Queensland: Is Data Driven Learning dead? In this talk Dr Crosthwaite ****
Language is never, ever, ever random
“Language is never, ever, ever random” (Kilgarriff, 2005), not in its usage, not in its acquisition, and not in its processing. (Nick C. Ellis, 2017, p. 41)

Nick C. Ellis (2017). Cognition, Corpora, and Computing: Triangulating Research in Usage-Based Language Learning. Language Learning 67(S1), pp. 40–65
Corpus of North American Spoken English (CoNASE)

The Corpus of North American Spoken English (CoNASE), a 1.25-billion-word corpus of geolocated automatic speech-to-text transcripts, is now available in a beta version.
URL http://cc.oulu.fi/~scoats/CoNASE.html for more information.
The corpus was created from 301,847 ASR transcripts from 2,572 YouTube channels, corresponding to 154,041 hours of video. The size of the corpus is 1,252,066,371 word tokens.
The channels sampled in the corpus are associated with local government entities such as town, city, or county boards and councils, school or utility districts, regional authorities such as provincial or territorial governments, or other governmental organizations.
The transcripts are primarily of recordings of public meetings, although other genres are also present. Video transcripts have been assigned exact latitude-longitude coordinates using a geocoding script.
This information was distributed through the Corpora-List by Steven Coats, University of Oulu, Finland
To cite the corpus, please use
Coats, Steven. 2021. Corpus of North American Spoken English (CoNASE). http://cc.oulu.fi/~scoats/CoNASE.html.
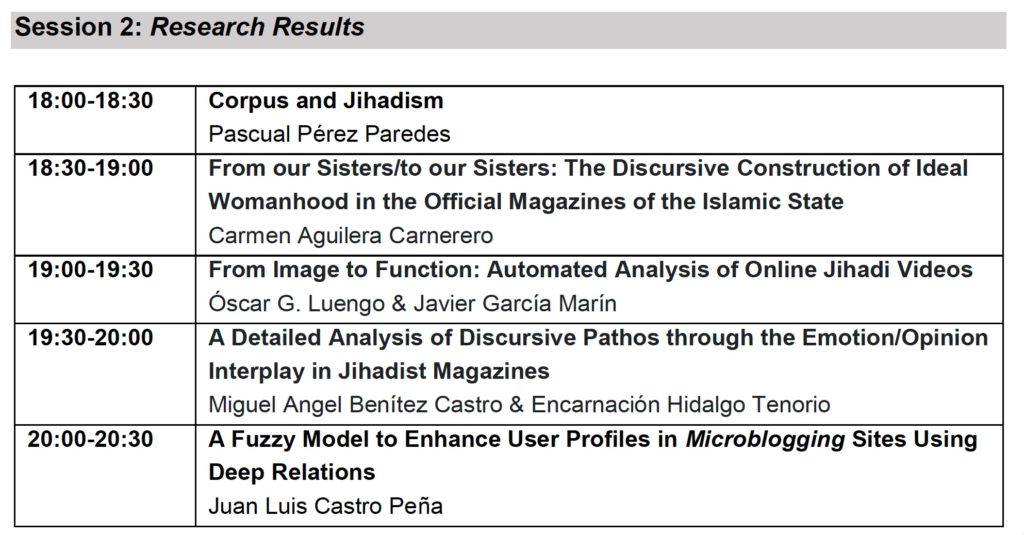
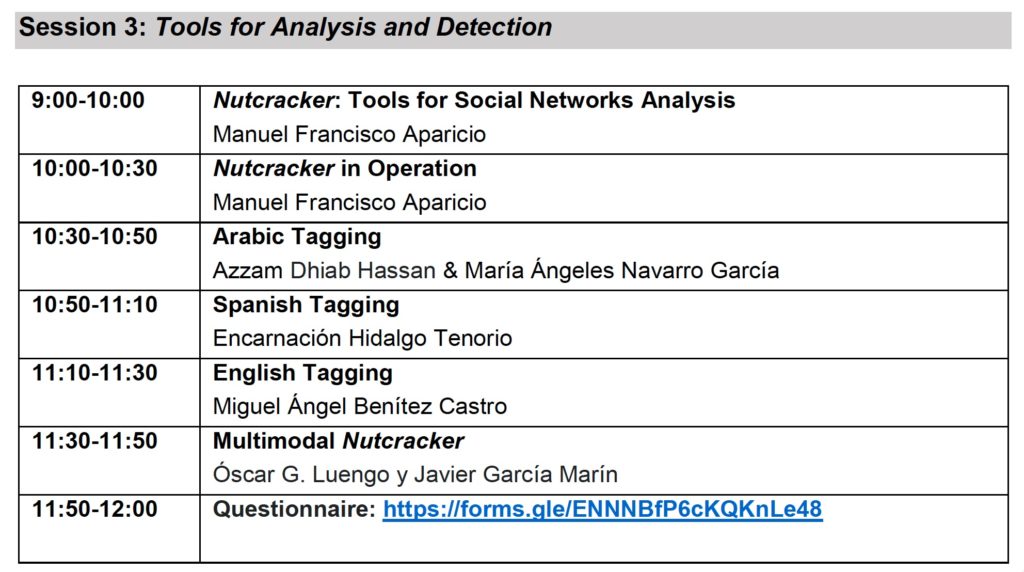
Jornada de difusión online proyecto de investigación Nutcracker, 24-25 junio 2021
NUTCRACKER: Sistema de detección, rastreo, monitorización y análisis del discurso terrorista en la Red Funded by: MINECO. 2017-2020. FFI2016-79748-R
Proyectos I+d+I – Programa estatal de investigación, desarrollo e innovación orientada a los retos de la sociedad.
“Nutcracker: System for Detection, Tracking, Monitoring and Analysis of the Discourse of Terror on the Net”

LINK 24 JUNE
https://oficinavirtual.ugr.es/redes/SOR/SALVEUGR/accesosala.jsp?IDSALA=22980794
Password: 657396

LINK 25 JUNE
https://oficinavirtual.ugr.es/redes/SOR/SALVEUGR/accesosala.jsp?IDSALA=22980797
Password: 466561
NUTCRACKER: Sistema de detección, rastreo, monitorización y análisis del discurso terrorista en la Red Funded by: MINECO. 2017-2020. FFI2016-79748-R
PIs: Prof Encarnación Hidalgo Tenorio, & Prof Juan Luis Castro Peña, Universidad de Granada


